Electronic waste (e-waste) contains printed circuit boards (PCBs) that are important carriers of precious metals and high-value materials. As the first critical piece of equipment in the resource disposal of e-waste, the electronic waste PCB shredder directly determines the recycling efficiency and economic benefits with its technical performance and process adaptability. The following is an in-depth analysis from the dimensions of equipment principle, core structure, technical parameters, process application, and maintenance system.
1. Equipment Working Principle and Technical Positioning
The electronic waste PCB shredder is based on the combined action mechanism of shearing, tearing, and crushing. It implements step-by-step crushing of PCBs, precious metal-containing electronic components, and other materials through the relative movement of movable and fixed knife sets, enabling the initial dissociation of metal and non-metal substrates. In the e-waste resource production line, this equipment undertakes the dual functions of "volume reduction + dissociation pretreatment" and provides raw material guarantee with uniform particle size for subsequent metal sorting and non-metal recycling processes.

2. Core Structure and Key Component Analysis
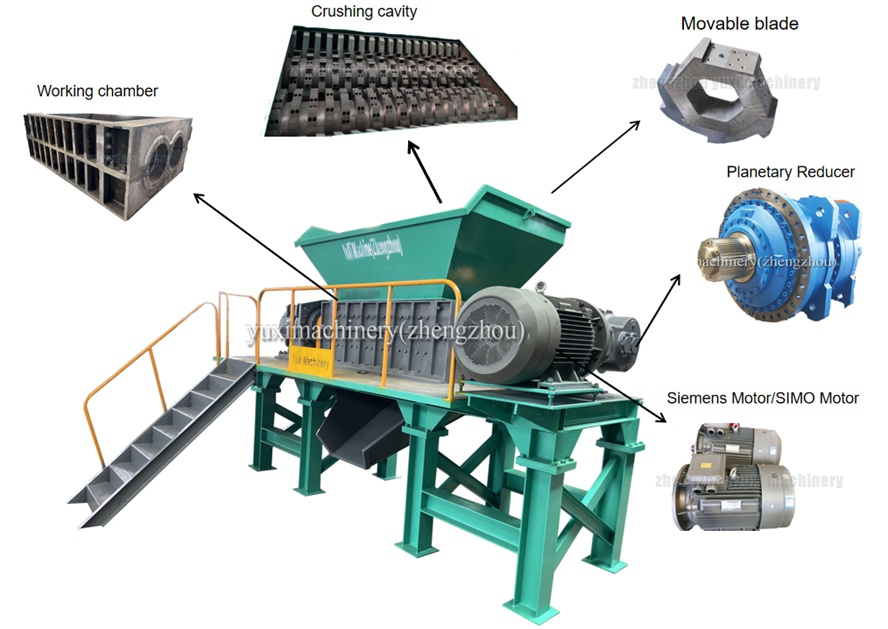
1. Crushing Cavity
As the core space for material crushing, the crushing cavity is integrally welded from ASTM A514 high-strength wear-resistant steel plates, and the inner wall is hardened (such as carburizing and spraying wear-resistant ceramics), which can resist the long-term impact of hard metal particles in PCBs. The cavity is equipped with multiple layers of movable knife sets (Movable Blade) and fixed knife sets. The movable knives are forged from AISI H13 high-chromium alloy tool steel, and their hardness reaches RC60 or above after vacuum heat treatment. They support multiple regrinding and repair, greatly reducing the cost of wearing parts.
2. Power and Transmission System
• Drive Unit: ABB or GE series motors are standard, and the power is matched according to the equipment capacity (usually 40-270hp). It has overload protection and frequency conversion speed regulation functions, and can adapt to the crushing needs of PCB materials with different humidity and density.
• Reduction Mechanism: A planetary reducer (Planetary Reducer) is used to convert the high speed of the motor into the low-speed and high-torque output of the crushing shaft (the speed is usually controlled at 50-150r/min), ensuring the strong crushing of hard PCBs.
3. Electronic Control and Intelligent System
It is equipped with a PLC microcomputer automatic control system, which can realize one-button start, stop, forward and reverse rotation, and overload reverse rotation of the equipment (it will automatically reverse to remove jams when the crushing cavity is blocked). The control system has a built-in sensor module, which monitors parameters such as bearing temperature and motor current in real time. When an abnormality occurs, it triggers an audible and visual alarm and shuts down the machine to ensure the safe operation of the equipment.

3. Technical Parameters and Process Adaptability
1. Key Performance Parameters
• Feeding Size: It supports a wide feeding range of 4-120 inches, and can directly process e-waste containing PCB components such as undismantled computer hosts and TV casings.
• Production Capacity: The single-machine capacity covers the range of 900-132,000 lb/h, and corresponding models can be selected according to the scale of the production line (such as small laboratory models and large industrial production line models).
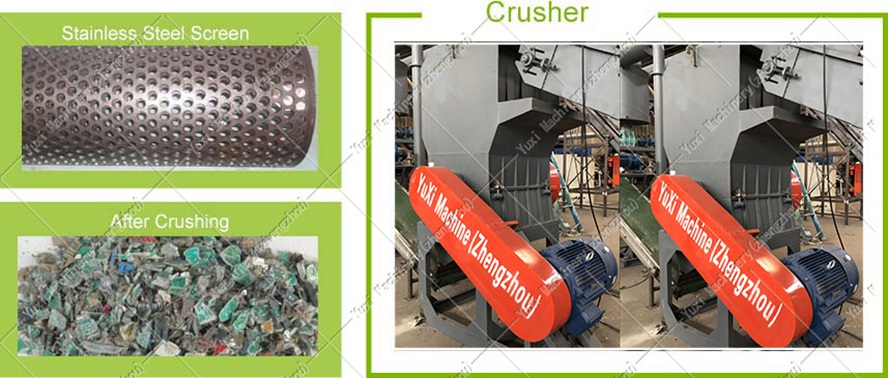
• Discharging Particle Size: By replacing 304 stainless steel screens (Stainless Steel Screen) with different apertures, the discharging particle size can be controlled at 0.2-2 inches (the typical value is 0.4-0.8 inches), meeting the strict requirements of subsequent sorting processes for material particle size.
2. Material Adaptation Range
In addition to PCBs, the equipment can efficiently crush the following e-waste and derivative materials:
• Materials with metal-plastic composite structures such as lithium battery cells and waste washing machine/refrigerator casings;
• Overall crushing of small electronic devices such as televisions and calculators;
• Pretreatment of light metal wastes such as metal barrels and color steel tiles.
4. Process Application in E-waste Resource Production Line
The electronic waste PCB shredder needs to form a coordinated process chain with subsequent sorting equipment. The typical production line process is as follows:
1. Dismantling Pretreatment: Separate large electronic components from the PCB body through a PCB dismantling machine (PCB dismantling machine);
2. Primary Crushing: The PCB shredder performs shear crushing on the materials to initially dissociate the metal pins, copper foil, and epoxy resin substrate;
3. Fine Crushing and Dust Removal: After further refining the particle size by a crusher (Crusher), the dust generated during the crushing process is collected by a pulse dust collector (Pulse Dust Collector);
4. Sorting and Recycling: Through equipment such as gravity separators (Gravity Separator) and electrostatic separators (Electrostatic Separator), efficient separation of copper, aluminum, precious metals (gold, silver, palladium) and non-metal powders is achieved;
5. Deep Processing: For the sorted plastic, rubber and other materials,精细化回收 is carried out through grinding equipment (Grinding machine).
5. Equipment Maintenance and Life Guarantee System
To ensure the long-term stable operation of the equipment, a hierarchical maintenance mechanism needs to be established:
• Weekly Inspection: Tighten all bolts and nuts, check the integrity of sensor leads, and test whether the reducer and motor work normally in terms of vibration and temperature rise;
• Monthly Inspection: Inspect the wear of the movable knife, fixed knife and crushing cavity at least once a month. If necessary, perform regrinding or local repair welding;
• Annual Overhaul: Conduct a comprehensive inspection of the PCB shredder, disassemble and clean the motor, reducer, and crushing roller bearings, clean the waste lubricating oil in the PCB shredder, and calibrate and upgrade the PLC control system.
6. Frequently Asked Questions (Q&A)
1. Q: What is the core difference between an electronic waste PCB shredder and an ordinary metal crusher?
A: The PCB shredder is designed for "metal-nonmetal composite structure" materials. The tooth shape and spacing of the movable and fixed knife sets are more suitable for the dissociation of the layered structure of PCBs; and it is equipped with a more precise screen and dust removal system to meet the requirements of e-waste recycling for dust control and particle size uniformity.
2. Q: Is special protection required when the equipment processes hazardous e-waste containing lead and mercury?
A: It is necessary to add a negative pressure air extraction interface to the crushing cavity and link it with the workshop waste gas treatment system; at the same time, operators need to be equipped with OSHA-certified dust and poison-proof equipment to ensure compliance with environmental and safety regulations for hazardous waste disposal.
3. Q: How to select the model of PCB shredder according to the scale of the production line?
A: It is necessary to comprehensively evaluate the daily processing volume of e-waste, the proportion of PCB materials, and the processing capacity of subsequent sorting equipment, and give priority to models with matching capacity and a certain redundancy (for example, for a production line with a daily processing capacity of 22 tons of e-waste, a shredder with a capacity of 4400 lb/h can be selected).
The technological iteration of electronic waste PCB shredders is promoting the transformation of e-waste disposal from "end disposal" to "resource recycling". Selecting suitable equipment and constructing a scientific process system are the core prerequisites for realizing the high-value recycling of e-waste.
 Shredding Machine
Shredding Machine
 Waste Recycling Line
Waste Recycling Line
 Optional Equipment
Optional Equipment



