A scrap metal shredder increases recycling value through 3 core methods: reducing material volume to lower transportation costs, purifying metal to boost raw material prices, and supporting environmental compliance to earn subsidies — the following analysis combines overseas cases and detailed key points.
What Is a Scrap Metal Shredder? Working Principle and Type Details
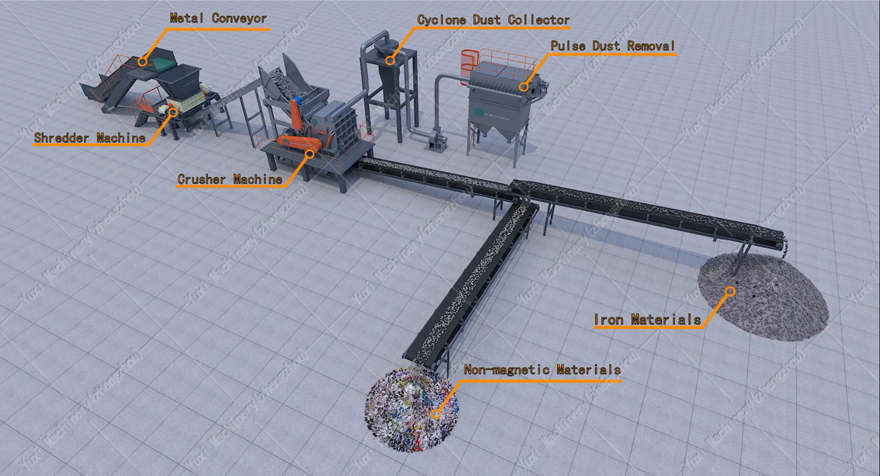
A scrap metal shredder is core industrial equipment that converts various scrap metals (such as end-of-life vehicles, industrial steel scrap, waste home appliances, and ship steel plates) into high-value uniform shreds. It uses the combined mechanical action of "impact + extrusion + shearing" from high-speed rotating hammers to break the original form of metal and separate impurities (such as plastic, rubber, wood, etc.) from the material, laying the foundation for subsequent magnetic separation, eddy current separation, and smelting processes.
Driven by global carbon neutrality goals, demand for such equipment grows at an annual rate of 12% (source: Global Recycling Association 2024 Report), as it can increase the recycling rate of scrap metal from 65% (traditional dismantling) to over 90%.
According to processing scenarios and material types, mainstream equipment is divided into three categories:
1. Heavy Steel Scrap Shredding System: Equipped with a high-torque motor of 750-1500 kW and wear-resistant high-manganese steel hammers (each weighing 50-100 kg), it targets heavy materials such as end-of-life vehicles, ship steel plates, and thick-walled steel pipes. The shredded material reaches a uniform size of 2-8 inches and can be directly fed into electric arc furnaces for steelmaking, improving smelting efficiency by 20% per ton compared to unshredded steel scrap.
2. Small and Medium-Sized Light-Gauge Material Shredder: Compact (occupying only 160-215 square feet) and energy-efficient (2-4 kWh per hundred pounds), it is suitable for light scrap metals such as waste home appliance shells, aluminum cans, and aluminum doors/windows. The processed material has a metal purity of over 95%, facilitating subsequent magnetic separation and eddy current separation, and is ideal for small and medium-sized recycling plants with a daily processing capacity of 11-55 tons.
3. Specialized Non-Ferrous Metal Shredder: Adopts low-speed (150-250 rpm) and high-shearing design, with rubber liners to avoid surface oxidation of metals. It mainly processes high-value non-ferrous metal scrap such as copper and aluminum, maximizing raw material purity — for example, when processing waste cables, copper recovery rate reaches 99%, far higher than the 85% of traditional incineration methods.
3 Core Values of Scrap Metal Shredders (With Overseas Cases)
1. Significantly Reduce Logistics and Smelting Costs
Case: A car recycling group in Birmingham, UK, introduced a 1500-horsepower steel scrap shredder in 2023. It reduced the transportation volume of end-of-life vehicles from 113 cubic feet per car to 28 cubic feet (a 75% reduction), cutting transportation costs from £95 to £28 per ton. Meanwhile, the shredded metal heats more evenly during smelting, shortening the smelting time per ton of steel from 45 minutes to 37 minutes and reducing energy consumption by 18%, saving over £1.8 million annually.
2. Increase the Market Value of Recycled Raw Materials
Case: A non-ferrous metal recycling enterprise in Osaka, Japan, uses an integrated "hammer + eddy current separation" shredder to process copper-aluminum mixtures from waste air conditioners. It increased copper purity from 91% (manual dismantling) to 99.6% (meeting electrolytic copper quality standards), raising the price per ton of copper by ¥18,000. Aluminum recovery rate also rose from 82% to 95%, creating an additional annual revenue of approximately ¥24 million.
3. Support Environmental Compliance and Carbon Emission Reduction
Case: An industrial waste treatment center in Melbourne, Australia, has used scrap metal shredders to process construction steel scrap since 2022, reducing solid waste landfilling by approximately 42,000 tons annually (equivalent to 1,200 tons of CO₂ emissions reduction). It also reduced soil heavy metal pollution (lead, cadmium, etc.) from open storage of scrap metal by 70%, earning an annual A$300,000 carbon emission reduction subsidy from the local government.

How to Select a Scrap Metal Shredder? 4 Key Judgment Points
1. Match Processing Capacity: For daily scrap metal processing of ≤50 tons, choose a small/medium-sized device with 1-5 tons per hour (cost: €80,000-€120,000). For daily processing of >100 tons, select a heavy-duty system with 10-20 tons per hour (cost: €300,000-€500,000) to avoid increased failure rates due to overloading.
2. Hammer Material Selection: For hard metals such as steel scrap and cast iron, use high-manganese steel or alloy hammers (service life: 800-1200 hours; replacement cost: 5-8% of the equipment’s total price). For non-ferrous metals such as copper and aluminum, use alloy steel hammers (hardness: Rockwell C 55-60) to avoid surface scratches affecting purity.
3. Control Output Size: For electric arc furnace steelmaking, choose an output size of 2-4 inches (optimal heat transfer efficiency during smelting). For non-ferrous metal separation, choose 0.8-2 inches (improves eddy current separation efficiency by 15% and air separation plastic impurity removal rate by 98%).
4. Focus on Energy Consumption and Environmental Indicators: High-quality shredders have an energy consumption of 1.5-2.3 kWh per hundred pounds of steel scrap (25% lower than traditional equipment). They also feature pulse baghouse dust collectors (dust emission ≤0.004 grains/cubic foot) and noise reduction devices (noise ≤85 dB) to avoid environmental fines.
Scrap Metal Shredder Operation and Maintenance: 3 Safety Regulations + 2 Maintenance Tips
Safety Regulations
1. Pre-Feeding Screening: Use metal detectors to remove flammable/explosive items (e.g., gasoline cans, lithium batteries) and impurities (e.g., concrete, wood) to avoid damaging hammers or causing safety accidents — a U.S. recycling plant once suffered over $100,000 in losses due to a fire caused by lithium batteries mixed into the feed.
2. Daily Wear Inspection: Check hammer wear every 8 hours of operation; flip or replace hammers when wear exceeds 30% of the original size. Check bearing temperature every 24 hours to ensure it does not exceed 158°F (excessive temperature reduces bearing life by 50%).
3. Comply with Safety Protection: Operators must wear hard hats, goggles, and ear muffs (equipment noise: 80-85 dB). Do not open the inspection door during operation; press the emergency stop button and cut off power immediately in case of emergency.
Maintenance Tips
1. Regular Lubrication: Apply lithium-based grease to bearings and gears every 24 hours (7-10 ounces per application) to extend equipment life by 30%.
2. Screen Cleaning: Clean screen blockages weekly to avoid reducing output efficiency — blocked screens decrease processing capacity by 20-30%.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Can scrap metal shredders process light metals like magnesium alloys?
No. Magnesium alloys generate high-temperature sparks during shredding, posing explosion risks. Additionally, scrap metals with toxic coatings (e.g., lead-based paint) must be stripped before shredding to avoid contaminating the final metal shreds.
2. What are the main operating costs of a scrap metal shredder?
Costs include electricity (≈30%, 50-80 kWh per ton of steel scrap), hammer and liner replacement (≈40%, hammers replaced every 1000 tons of steel scrap processed), and labor/maintenance (≈30%, requiring 2-3 operators). The total operating cost per ton of steel scrap is approximately $15-$25.
3. What is the payback period for small recycling plants deploying scrap metal shredders?
In the European market, a small shredder with 2 tons per hour capacity costs €80,000-€120,000. Operating 8 hours daily, it increases the value of each ton of scrap metal by €30-€50 (from "bulk price" to "pure metal shred price"), generating daily revenue of €480-€800. The payback period is approximately 12-18 months.
4. How to solve dust and noise problems of scrap metal shredders?
Dust can be controlled with pulse baghouse dust collectors (filtration efficiency: 99.9%, dust concentration ≤0.002 grains/cubic foot). Noise can be reduced to ≤80 dB by installing shock pads under the equipment (10 dB reduction), soundproof panels in the workshop (15 dB reduction), and soundproof enclosures around the shredder (20 dB reduction).
5. How often do scrap metal shredder hammers need to be replaced?
For steel scrap processing, high-manganese steel hammers have a service life of 800-1200 hours. For non-ferrous metal processing, alloy steel hammers last 1500-2000 hours. Replacement time depends on material hardness and processing volume; shredding efficiency drops by >15% when hammer wear exceeds 30% of the original size, requiring replacement.

A scrap metal shredder is not only an "efficiency engine" in the scrap metal recycling process but also a core pillar of the global circular economy. Through three core values — volume reduction and cost reduction, purification and value increase, and environmental compliance — it helps enterprises achieve a win-win of economic and environmental benefits amid resource constraints.
 Shredding Machine
Shredding Machine
 Waste Recycling Line
Waste Recycling Line
 Optional Equipment
Optional Equipment



